When Wil the Mauna Loa Erupt Again

Radar image of Mauna Loa taken from space shuttle Endeavour in 1994. Colour indicates surface roughness, where red is smooth (pahoehoe lava) and white is rough (a'a lava). source: JPL
Mauna Loa keeps paradise interesting. It has erupted 33 times since 1843, with big eruptions happening on average one time every 8 years. Over that time it has covered its slopes with 4 km3 of new lava. Only those are only the nigh recent stirrings. Its older lava flows cover over half of the island of Hawaii. Merely after the large eruption in 1950, Mauna Loa became remarkably quiet. There have been only 2 eruptions since, 1 of which (1975) lasted less than ane 24-hour interval and was the second smallest eruption of the 20th century. There was i meaning eruption in 1984, but nothing since. Simply now the largest volcano on World is stirring. Aggrandizement shows that magma is accumulating, but south west of the elevation. Earthquakes are a daily occurrence and HVO has raised the alert level. There is problem brewing in paradise.
Mauna Loa is the world's second tallest volcano on Earth, later Mauna Kea. It started 5 km beneath the sea, taking peradventure a one thousand thousand years to achieve its current elevation of 4.17 km above sea level. The total pinnacle, from base to summit, is therefore over 9 km, more than Mountain Everest. To compare, the highest volcano on Earth is Ojos del Salado, on the Chile/Argentina edge, which reaches 6,893 chiliad above bounding main level. Mauna Loa is slightly cheating since the part that is under water benefits from the up pressure level from the h2o – it floats a scrap. I can correct for this, and calculate how loftier a mountain would be that has the same pressure at its base, without the aid of water: this reduces Mauna Loa by 1800 m, and gives an equivalent elevation of 7200 m, almost the aforementioned as Ojos de Salado. This may not be entirely accidental. There is only and so much weight a rock can bear, and both volcanoes will consist of very similar types of rock at their base. Rocks at the bottom, nine km below the height, are in danger of being crushed by the weight. On Mars, gravity is iii times less and the same weight corresponds to a mountain iii times taller – 22.5 km tall. In fact, Olympus Mons stands 22 km above the surrounding plain, virtually exactly this number. So it seems this is indeed nearly the tallest a volcano can get. Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea are almost the same top, differing by only 24 meter. They are running into their limits.
Although it is slightly lower, Mauna Loa is a lot bigger than Mauna Kea. Mauna Loa is a shield volcano: its fast flowing lava has spread far, edifice a big mountain with a shallow slope. It is much wider at its base than Mauna Kea, has much more book and therefore much more mass. Mauna Loa, the largest volcano on Earth, is and so large, it is very hard to meet. You tin't see it to a higher place the horizon: it IS the horizon. I remember reading the story of someone in Africa trying to chase an elephant out of their garden at night. In the flash light she failed to see any elephant, only the greyish sky. Only then did she realize the sky was the elephant, and then large the eye couldn't see it. Mauna Loa is this proverbial elephant. The only identify from where y'all tin can get a good feeling for its tremendous size is from the summit of Mauna Kea (non an easy place to get to either.) From here, at dark sometimes you can see the distant, angry eye of Pu'u'O'o, just in the day Mauna Loa dominates the sky line. (Unexpectedly for an astronomical observatory, y'all tin can't see the stars that well from Mauna Kea. It is as well loftier and the eye and the brain are badly afflicted past the lack of oxygen. You become one-half bullheaded and too dim to realize.)

Mokuaweoweo crater, with south west rift in the foreground
The tiptop of Mauna Loa has its crater, chosen Moku`aweoweo Caldera. It consists of 3 partly overlapping craters, of which the key one is the largest. Together they are 6 by two.v km in size. The caldera isn't that former. It formed because of a large flank eruption which emptied the shallow magma reservoir. This was the eruption which formed the Pana`ewa flow field, which Hilo is build on.

Lava flows from Mauna Loa. Hilo is front middle, Mauna Kea right. Reddish and orange are flows since 1832.
Mauna Loa is a very elongated mountain, much longer in the s west-north east direction. In fact, the name Mauna Loa ways 'long mountain'. The long ridge follows a double rift zone. There is a caldera at the superlative (showing the mountain used to exist a little higher); the rifts extend from the caldera towards the south westward and towards the eastward, running from the south eastern point of Hawaii to (virtually) Hilo, a distance of close to 100 km. The s w rift bends past 40 degrees where it reaches an altitude of 2400 yard. At this point a number of eruptions have build a satellite shield.
Mauna Loa eruptions tend to brainstorm near the elevation, simply quickly migrate to the rift zones, down slope. Both rifts can erupt anywhere along their length. Private rift eruptions can occur along a section as short as tens of meter, to a staggering 20 km (as happened during the large 1950 eruption). Individual eruptions typically last a calendar week, erupt 0.2 km3 of lava and cover 20 kmii. The lava moves fast, roofing up to 5 km per hr on the steepest slopes, and can reach the bounding main (on the west and south side, at least), in less than a day.

Map showing areas covered by `a`a lava flows erupted during the eruption of Mauna Loa between March 24 and April fifteen, 1984. Source: HVO
The 1984 eruption is a good example. Information technology began three years earlier, with slowly increasing earthquake action, culminating in an M6.6 event. Near v months afterwards this, 25 March 1984, the eruption began, after 2 hours of tremors, initially at the meridian, only within hours the eruption migrated commencement to the south west rift zone, changed its mind and moved to the n east rift zone. A few hours later, lava curtains erupted 7 km from the summit, and later that twenty-four hours, the eruption moved to a ii km section 10 km from the tiptop. From here lava flows quickly advanced to Hilo. Somewhen the menses reached a length of thirty km, coming to within 7 km of Hilo. As the eruption diminished, the active lava stayed closer to the point of eruption. Afterward some tense days, the eruption ended on April 15.
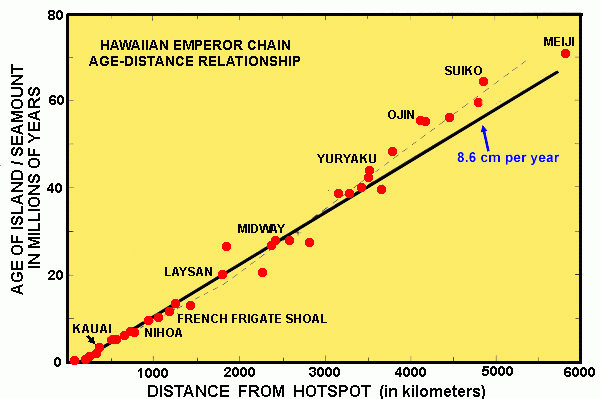
Hawaiian Archipelago: trail of a hot spot
Hawaii is at the terminate of a long chain of islands and sea mounts. Shut to Hawaii are the Windward islands, or Hawaiian archipelago. Farther away are the Leeward islands, terminating near Midway. Across that, the chain becomes a series of bounding main mounts, which makes an bending of 120 degrees with the other chain: these are called the Emperor sea mounts (named after Japanese emperors). The mounts get progressively older farther from Hawaii, with the oldest one about 80 million years. The chain terminates at the Obruchev Rise, very close to the Aleutian subduction trench, where information technology meets Kamchatka. There may have been more, older ocean mounts, at present subducted into oblivion.

The Hawaiian concatenation is the blazon specimen of a hot spot chain. The hot spot is supposed to have been stationary or about stationary, while the Pacific plate drifted over it. The precipitous bend in the chain shows a sudden change of management of the Pacific plate, well-nigh 45 million year agone. Previously, the plate was going north, but now it is moving to the north westward. What caused this change? That is not really known. Information technology happened at about the time India collided with Asia, and perhaps this is related although that was quite a distance away. Information technology may besides have been caused by the onset of subduction along the Asian plate purlieus. Afterward the change of direction, for a few million years no islands were formed.
Hot spots may come from plumes deep into the pall, or they can be shallower, affecting mainly the upper mantle. Opinions differ. In the case of Hawaii, seismographs, used to map out the mantle, have detected the hot region to 1500 km depth, perchance more. That is one-half the depth to the core-mantle boundary. It seems likely information technology extends to the bottom of the mantle. It came from the deep. Merely other data do non agree, and a more recent report has only establish a pancake of heat, underneath the chaff, not extending into the deep.
In any instance, non all the lava it erupts comes from the deep curtain. It seems that over time, Mauna Loa has erupted a decreasing fraction of 3He, and that is a sign that a fraction of recycled crust is beingness included in the magma. Perhaps equally the hot spot is moving away (and Mauna Loa is no longer straight over it, as it was when information technology began), the magma includes an increasing amount of shallower melt.
How and where did the hot spot get started? Its origins have sadly been lost in the subduction trench. Or possibly not. Could the hot spot take started at the Obruchev Rise? The Ascension is near an old spreading centre, abased in the Cretaceous when the middle jumped northward. The ridge was at the western edge of the Fallaron plate, which has since largely been subducted underneath America. This puts the hot spot, at its earliest known location, straight underneath this spreading ridge. Much like Iceland! Did the spreading centre beginning the plume? Or did the feather split the plate? This is solidly in the realm of speculation. But information technology is interesting to call up of tropical Hawaii starting off like Republic of iceland. Possibly there is promise for Reykjavik.
During its 80 one thousand thousand year history, the eruption rate has been remarkably constant, at about 0.015kmiii per year. For comparing, over the past 200 years the eruption charge per unit has been most 0.023km3 per year from Mauna Loa. Kilauea's eruption rate should be added, which doubles the amount. Then the current rate of activity is a bit higher up boilerplate for the hot spot.
Science
Volcanoes provide a very temporary surface and are not the best place to build expensive structures. A skilful case was the Etna volcano observatory, build too close and unfortunately destroyed by the lava they were trying to observe. They wisely relocated to Catania, for safer viewing. It is surprising to find a scientific institute located well-nigh the top of Mauna Loa, and even more than surprising that it is not there to study the volcano. The Mauna Loa Observatory studies our air and our Sun – not the shaky ground underneath their anxiety.

>The Mauna Loa Observatory. In the background is Mauna Kea – Mauna Loa is behind you lot.
The Observatory is located 5 km north of the summit, 700 meter below information technology. Information technology is and so high upwardly in order to stay away from any pollution (natural or otherwise) coming upwardly from below. The inversion layer in the atmosphere usually keeps that locked up. The air comes in from the sea, again as clean as anywhere on Earth. It is an ideal pace to measure out how our air is changing. Since 1956 the amount of CO2 in our atmosphere has been measured. At that place are several places around the globe where this is done, only Mauna Loa has the cleanest record. The buildings, offices and domes are build on stark, blackness lava fields and even afterward 50 years, gives an impression of a temporary incursion in an unforgiving state. The total lack of any vegetation is an advantage, equally plants impact the local CO2. The famous Keeling curve, showing how rapidly nosotros are changing our atmosphere, is measured here, a monument to our fragility and willingness to accept inordinate risks. Information technology fits the environment, but if Mauna Loa were to erupt this management, the scientists may only have an hour to become away. There is also a solar observatory here. In general, only astronomers put their most expensive instruments on height of agile volcanoes. A certain condone of the globe they alive in may play a office. At that place is a massive astronomical observatory on Mauna Kea. Again, their only access route goes over the recent flows from Mauna Loa. 1 could question the wisdom of building the one escape route where it is well-nigh likely to be cut off.

The Keeling curve
The mid-life crunch of Mauna Loa
I mentioned that Mauna Loa seems to be losing its hot spot. How do we know? Part of the evidence comes from the changing isotopes, the reducing fraction of 3He compared to 4He. But there is a more straight indication. Mauna Loa has stopped growing.
Mauna Loa'due south lava covers one-half of Hawaii, to the coast and into the sea. The eruptions still often reach the bounding main, at to the lowest degree on the westward side of the isle, merely they only rarely reach the Hilo expanse, even though this surface area is entirely build on Mauna Loa's lavas. Over the by 100,000 years, the lava flows have not been as vigorous and have not reached equally far as previously. Withal, Hilo should non be conceited. In 1880 lava reached with 2 km of Hilo Bay.
How far lava can flow depends on the cooling charge per unit. The menstruation stops where the lava solidifies. The college the flow rate, the slower the cooling (big bodies stay warm for longer), and the further the lava flows achieve. This process is very clear in Kilauea. When the eruption rates go upwardly, the lava flows extend, as they did last year. When they turn down, lava stays closer to the signal of eruption, mostly less than five km this yr. Holuhraun did the aforementioned affair: when the flow began to diminish, the catamenia field stopped expanding. Lava from Mauna Loa now rarely reaches Hilo Bay, perhaps simply one time per 4000 twelvemonth. It more often than not stops 5-ten km from Hilo. One flow did cover the entire urban surface area and the bay, perhaps one thousand yr agone, simply this one erupted from a vent very close to Hilo to begin with. Most of the lava now flows closer to the rift, and less lava reaches the sea. This makes the mount abound steeper: information technology is beginning to enter its post-shield phase. This may exist related to the growth of Kilauea, competing with it for lava resources.
The weight of the mountain pushes the crust beneath down. The whole island subsides, at effectually two mm per year. Then far lava degradation has just about kept up with this, but it may not for much longer. The billy is existence passed and Mauna Loa volition sink.
The 30-yr silence of Mauna Loa has coincided with the continuing eruption of Kileauea at Pu'u'O'o. This eruption started in 1984 and is yet going. But eruption rates take slowly declined. The fundamental crater of Kilauea shows inflation and this may be due to an ebbing period through to Pu'u o'o. It is argued that Mauna Loa and Kilauea are separate volcanoes, from 2 different hotspot tracks, Kilauea connecting to Mauna Kea. This seems less probable, and although the feed systems are not identical, they are not independent either – they are besides shut together. The question will be settled soon: if they are contained, a Mauna Loa eruption would non affect Kilauea. If there is connection between them, you would see Kilauea changing when Mauna Loa erupts. Will in the future Kilauea take over and rival Mauna Loa in size? Maybe they really are too close. At that place is another candidate waiting out at ocean, which is more likely to get the next giant.
Towards eruption?

Afterwards xx years, activity underneath Mauna Loa resumed in 2004, with a series of deep earthquakes. The mountain began to inflate at the same time. Things calmed down again, simply in 2014 earthquakes moved to shallower levels, and inflation increased. Magma is now accumulating at three-five km depth, below the south west rift. Action is standing at an elevated but non-disquisitional level: it has all the appearance of building up to an eruption, only it does not announced to be imminent. Volition it be a twelvemonth, five years, longer? Afterward the previous burst, in 2004, nothing happened for a decade. The current episode could equally go off the boiler. But the magma is now shallower, and the inflation more focussed. This is offset to look as if it is closer to deciding to erupt.

Inflation and earthquake action at Mauna Loa. Source: HVO
An eruption is probable to get-go within hours of strong tremors. Initially it volition exist close to or at the meridian, before apace migrating. Equally the current aggrandizement is a petty south west, the almost likely migration is in this direction. The lava could period either side of the ridge. For a normal-size eruption, Highway 11 will be cut within one or two days, possibly at several locations if the eruption is big, and lava will flow into the ocean shortly later. Judging from the time line of the diverse flows since 1843, Kealakekua Bay would seem side by side but this is judge work – Mauna Loa does non work similar that. Equally the magma chamber empties, the take a chance of larger, possibly damaging earthquakes increases. The southward side of the mountain is decumbent to slipping and the risk of this increases when the pressure level changes. Conversely, earthquakes can besides affect internal magma flows and an convulsion tin hasten or stop an imminent eruption. The double 1868 earthquake (M7.1, M7.9) disrupted the magma supply for decades.
Purely based on the past record, in that location is a 50% run a risk of an eruption within 8 years. I would look something inside a decade, nearly likely from the south west rift zone. When it happens, it would be advisable to run abroad, and not, equally Hawaiians normally practise, run towards the eruption to get a ameliorate view. Mauna Loa is not like Kilauea. It is fast and furious, all-time viewed from a large distance. Paradise tin wait.
Background reading
Hawaiian Volcano Observatory; Much of the material and several figures in this post came from them
Hawaii'south island concatenation, with exam questions at the cease! Source of some of the figures and material used in this mail
Source: https://www.volcanocafe.org/trouble-in-paradise-awakening-mauna-loa/
0 Response to "When Wil the Mauna Loa Erupt Again"
Post a Comment